The final 2025 edition of the SCImago Media Ranking (SMR), the winter wave, completes for the first time the representation of the global media ecosystem and strengthens the accuracy of the Digital Reputation Index (DRI)
The SCImago Media Ranking closes 2025 with the most comprehensive sample since its inception, driven by the incorporation of radio as a new media type. This edition marks the end of a phase of sustained expansion that has led the ranking to grow by 36% from its first edition in 2022 to more than 6,500 media outlets in the most recent wave.
Since its launch, the SMR has evolved from a classification focused on legacy and native press into the first global map of the contemporary communication ecosystem. Successive editions have progressively expanded the scope of the project to integrate general-interest press, business and sports media, television, and now radio, thereby reinforcing the original objective of comprehensively mapping the presence and visibility of media in the digital environment.
The historical trajectory illustrates this progress clearly: in 2022, the sample included more than 4,500 newspapers in 90 languages; in 2023, analyses were introduced on the prevalence of the printed press, the linguistic hegemony of English, and regional media behavior; and in 2024, two decisive categories—sports and business—were added, along with new filters that allow navigation by typologies, levels of coverage, and platforms.
The 2025 edition culminates this process by integrating all radio broadcasters identified at a global scale and by adding a new content category—music—thus reinforcing the presence of radio within the ranking and completing, for the first time, the representation of both traditional and digital media. Television also gains greater prominence compared to previous editions, consolidating itself as one of the most robust blocks within the ranking.
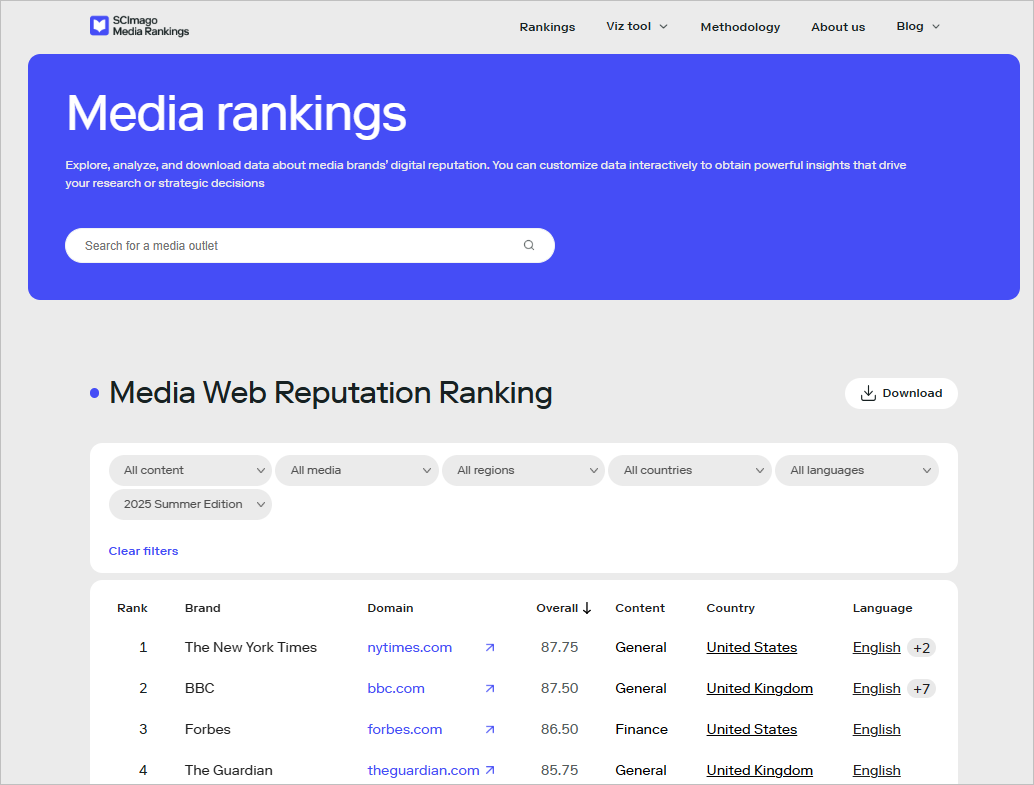
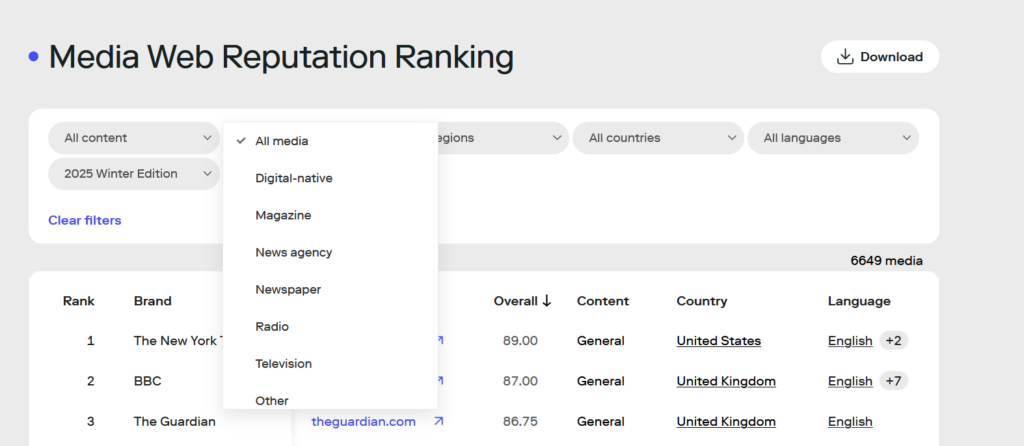
Specifically, the SMR currently includes 6,649 media outlets and offers a set of variables that allow the media ecosystem to be analyzed from multiple perspectives, facilitating comparative studies and more precise analyses of the influence, reach, and diversity of media organizations worldwide.
The first category corresponds to the type of content produced by the media outlets included in the sample. This variable distinguishes between general, musical, financial, sports, and cultural content, making it possible to identify which informational areas concentrate greater prestige and impact in the digital environment. From a research perspective, this classification is particularly useful for analyzing thematic specialization among media and for studying which types of content generate greater visibility and reputation depending on the social and economic context.
The second category refers to the type of media, differentiating between digital-native media, magazines, news agencies, newspapers, radio stations, television channels, and other typologies. This variable allows observation of how different media formats are positioned within the ranking and enables comparisons between the performance of traditional and digital media. It also provides relevant insights into media adaptation processes to the online environment and into the evolution of news consumption according to platform.
Third and fourth, the ranking incorporates the variables of region and country, which make it possible to segment results geographically. These categories facilitate a more detailed analysis of the media landscape in specific areas, enabling comparative studies between countries or regions and the examination of inequalities, concentrations of media power, or informational particularities according to geopolitical context. For academic research, these variables are key to contextualizing data and avoiding overly homogeneous global interpretations.
Finally, the language variable adds a linguistic dimension to the analysis of the ranking. Identifying the predominant languages in the international media landscape allows reflection on the importance of language as a vehicle for communication and as a factor of reach and influence. This category is particularly relevant in countries or regions where media use non-native languages or languages with greater international projection, which can directly affect their visibility, reputation, and capacity for global dissemination.
Taken together, these variables make the SCImago ranking a particularly valuable tool for communication research, as it not only orders media by impact but also enables exploration of the cultural, linguistic, geographic, and structural dynamics that shape the current digital media ecosystem.
The SCImago Media Ranking is a joint project of the Universities of Granada, Navarra, and Pompeu Fabra, developed by SCImago Lab. Its aim is to provide a rigorous and accessible tool to understand the global information ecosystem through comparable metrics. The full methodology of the DRI can be consulted at scimagomedia.com/methodology.